
Blowout Preventer: Key Components and Functions
2024-02-16 10:00Blowout Preventer: Key Components and Functions
The blowout preventer (BOP) holds a pivotBOPal role in well control, particularly during underbalanceblowout preventerd drilling operations. Its primary objective is to securely close the wellbore under pressure, maintain continuous well control, and facilitate the circulation of formation fluids entering the well.
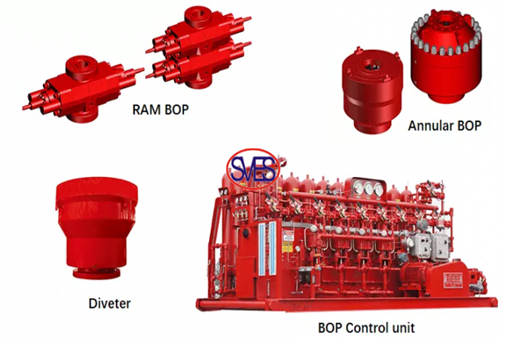
Hydraulic blowout preventers primarily come in two forms: ram blowout preventers and annular blowout preventers. The ram blowout preventer consists of essential components such as the shell, side door, oil cylinder, cylinder head, piston, piston rod, locking shaft, seal, and ram. Its operational mechanism involves utilizing hydraulic pressure to drive the piston, thereby opening or closing the gate and achieving the desired wellhead closure or opening.
The ram, a crucial part of the ram blowout preventer, encompasses four types: full-sealed, half-sealed, variable diameter, and shearing. These various ram types cater to different conditions, with the semi-sealed ram capable of closing specific pipes like drill pipes and tubing, allowing the suspension of drilling tools if needed. The fully sealed ram, when no pipe tool is present, can completely seal the wellhead. Under unique circumstances, the shear ram can effectively cut off the drilling tool. Additionally, the flange outlet on the shell's side facilRam BOPitates drilling fluid circulation and choke-killing operations.

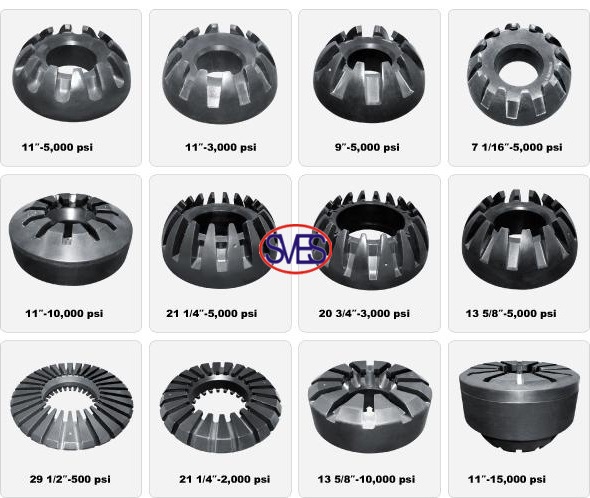
Annular blowout preventers come in two types: cone annular blowout preventer and spherical annular blowout preventer. Their structure includes the shell, top cover, rubber core, and piston. These preventers use a rubber core to close the annular space when drilling tools, tubing, or casing are present in the well. In the absence of drilling tools, they can fully seal the wellhead during various operations like drilling, coring, and testing.
Both annular blowout preventer types operate similarly. High-pressure oil from the control system enters the lower closing cavity to push the piston upwards, causing the rubber core to move and achieve sealing. When the well needs to be opened, the piston descends, and the rubber core resets, allowing the wellhead to open.
Installed on the wellhead casing head during oil drilling, blowout preventers control high-pressure oil, gas, and water blowouts. When well pressure is high, the blowout preventer can shut down the wellhead. It also features a four-way under-ram that, when mud is pressed into the drill pipe, can replace gas-invaded mud, increase liquid column pressure, and suppress the ejection of high-pressure oil and gas.

Various types of blowout preventers exist, including ordinary, shear, and rotary blowout preventers. Ordinary blowout preventers are activated in emergencies to handle different-sized drilling tools and empty wells, while rotary blowout preventers facilitate blowout and drilling operations. In deep well drilling, combinations of two ordinary blowout preventers, shear blowout preventers, and rotary blowout preventers are often employed.
Annular blowout preventers, often paired with ram-type blowout preventers, create a sealed annular space between the pipe string and the wellbore during operation. While it can also function independently when a pipe string is present, long-term shut-in use is not recommended after a few operational cycles.
